Main Menu
Ultrasonic Transducer Driver Amplifier Circuit
суббота 02 марта admin 0
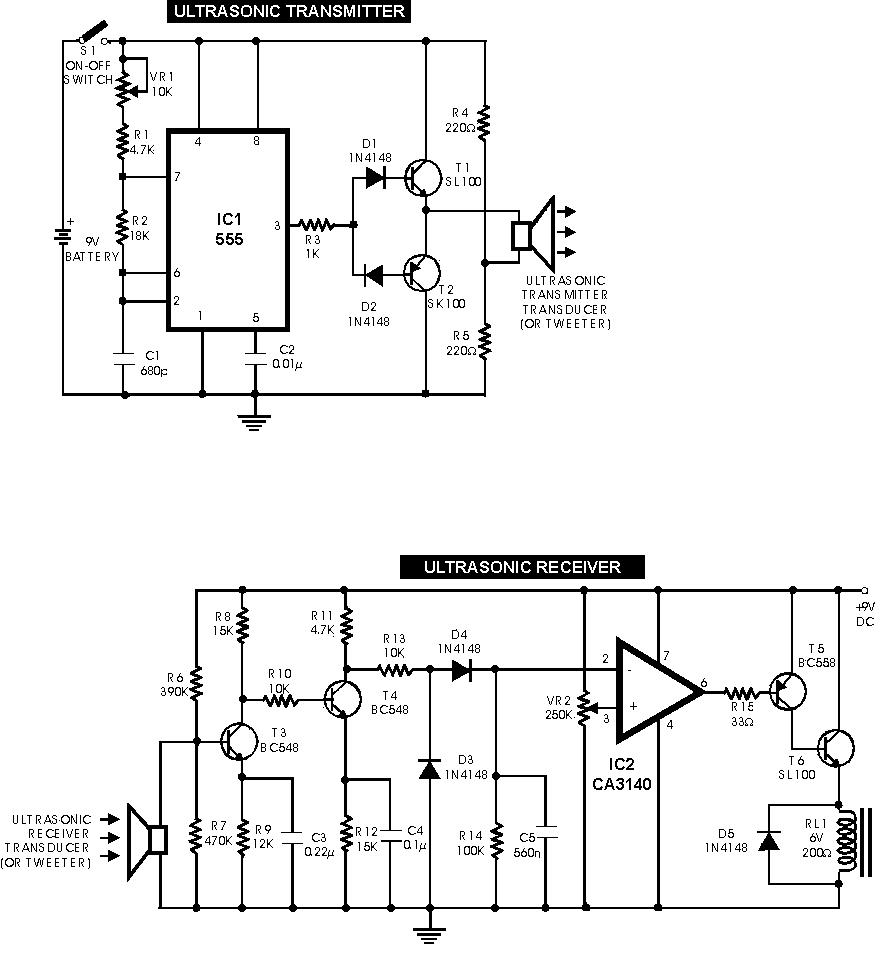
Ultrasonic transducer driver circuit ultrasonic transducer driver circuit on ultrasonic cleaning workpiece, the ultrasonic generator PCB are allowing the particles attached to the workpiece, oil and other mechanical vibration with the ultrasound off or dissolved or emulsified and so on, to achieve the purpose of cleaning the workpiece. Ultrasonic Cleaning Equipment Ultrasonic parts of divided into two parts; one ultrasonic transducer, said ultrasonic vibration (or head); the other is the ultrasonic generator, ultrasonic transducer is the ultrasonic generator is converted to electrical signals provided by the mechanical vibration. Clipp store 2017 + serial. Ultrasonic transducer driver circuit.
We have developed a portable high power ultrasound system with a very low output impedance amplifier circuit (less than 0.3 Ω) that can transfer more than 90% of the energy from a battery supply to the ultrasound transducer. The system can deliver therapeutic acoustical energy waves at lower voltages than those in conventional ultrasound systems because energy losses owing to a mismatched impedance are eliminated. The system can produce acoustic power outputs over the therapeutic range (greater then 50 W) from a PZT-4, 1.54 MHz, and 0.75 in diameter piezoelectric ceramic. It is lightweight, portable, and powered by a rechargeable battery. The portable therapeutic ultrasound unit has the potential to replace “plug-in” medical systems and rf amplifiers used in research. The system is capable of field service on its internal battery, making it especially useful for military, ambulatory, and remote medical applications.
Aug 13, 2014 - flow in Ultrasonic transducer single channel receiver amplifier circuit. Amplifier circuit laser diode driver circuit ultrasonic generator circuit.
Driving circuit The circuit for the low-output-impedance driver is shown in Fig. A pin driver (EL71581SZ, Intersil, Inc.) that is capable of driving high capacitive loads is supplied with a 5 V square wave TTL input at pin 3. The input timing signal comes from a 1.54 MHz crystal oscillator (SE1216-ND, Epson Toyocom, Inc.) that fits the ultrasound probe’s resonant frequency for maximum power transfer. Pins 1 and 8 are held at +12 V with 47 and 0.1 μF bypass capacitors to ground. Pin 2 is connected to pin 1 with a 10 kΩ resistor. Pins 4 through 6 are connected to earth ground.
Pin 7 of the pin driver is the output that provides a 12 V square wave to regulate the switching of the metal-organic-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) voltage drain. From pin 7 of the pin driver a 2.2 Ω resistor splits off with two 0.1 μF coupling capacitors into the input pins 2 and 4 of the low on resistance N∕ P channel MOSFET (IRF7350, International Rectifier, Inc.). Pins 1 and 3 of the MOSFET are held at a maximum of −50 and +50 V, respectively, with 820 Ω resistors across pins 1–2 and 3–4. A 47 μF and a 0.1 μF bypass capacitors to ground are applied as well to pins 1 and 3 of the MOSFET. Pins 5–6 and 7–8 of the MOSFET are tied together and coupled through 1 Ω, 5 W power resistors with the output drive signal applied to the ultrasound transducer through a standard BNC connector. Circuit schematic of the low output impedance ultrasound driver.
A pin driver is appropriately timed with a TTL 5 V signal from a 1.54 MHz crystal oscillator that switches the drain of the low output impedance MOSFET from ±50 V maximum. The Intersil, Inc. EL7158ISZ pin driver acts as the logic switch for the MOSFETs that supply the power oscillation drive to the ultrasound transducer. For high power continuous wave applications requiring high current, pin drivers are used to switch MOSFETs in parallel to lower the current burden on each MOSFET. As shown in Fig., a single timed pin driver at 5 V drives two pin drivers at 12 V as a branching cascade to switch four MOSFETs each for the portable high power ultrasound driving system. Each pin driver∕MOSFET unit is wired as shown in Fig. The output impedance of the driver was measured directly, and determined from manufacturer values of the MOSFETs, and eight 1 Ω parallel resistors to be almost entirely resistive and approximately 0.2–0.3 Ω.
System design Figure shows a schematic of the complete system, and Fig. Is a photograph of the finished device. Figure is divided into the battery supply and user control portion (left), TTL logic timing signal (middle yellow box), and parallel MOSFET ultrasound driving stage (right red box). The system is housed in a 4×6×2 in. 3 watertight plastic enclosure (No.